
A Basic Guide to Female Anatomy
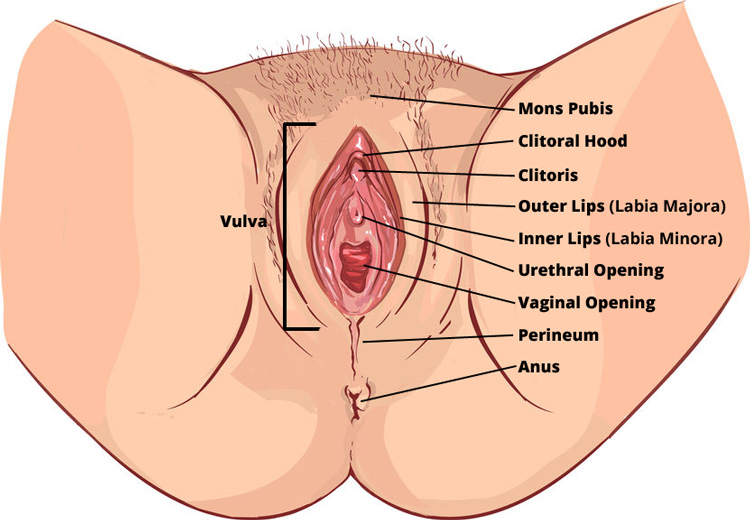
Vulva
"Vulva" is the global term that describes all of the structures that make the female external genitalia. The components of the vulva are the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, urethra, and vaginal opening.
Mons pubis
The mons pubis is the fleshy area on the pelvic bone. It functions as a source of cushioning during sexual intercourse.
Clitoris and Clitoral Hood
The clitoris (similar to a man's penis) is a sex organ in females that functions as a sensory organ. The glans clitoris has many blood vessels and thousands of nerve endings. It is protected by the clitoral hood – a fold of skin that surrounds and protects it.
Labia Majora
"Labia Majora" refers to the larger lips.
Labia Minora
"Labia Minora" refers to the smaller, inner lips. (Most often when labiaplasty is discussed, the focus is on the appearance of the labia minora.)
Urethra/Urethral Opening
The urethra allows the bladder to empty urine to the outside.
Vagina/Vaginal Opening
The vagina is the muscular tube that connects the cervix to the external surface. (Prior to a woman's first sexual experience, it may be partially covered by the hymen – a thin membrane.) The function of the vagina is for sexual intercourse and childbirth.
Perineum
The perineum is the area between the vulva and the anus.

